Marketers once took weeks to build campaigns. One idea needed hundreds of variations. Testing dragged on. Approvals lingered. Not now.
Retailers using AI for targeted ads are getting 10% to 25% more returns on their advertising money, and global spending on AI marketing technology is expected to hit $82 billion in 2026. The technology changed from being something new to being very important in less than two years.
This article looks at how generative AI is changing marketing and branding using real examples, clear results, and useful applications.
What Generative AI Means for Marketing
Generative AI generates new information based on learned patterns. The technology employs large language models trained on massive datasets to create text, images, videos, and audio.
Classical AI provided predictions on data. Generative AI actually generates things. That difference is important because generating things has always been the biggest hurdle within the realm of marketing operations. More than 37% of the marketing departments incorporated AI into an integral component of the strategy. The technology handles three key marketing jobs:
Content generation automates copywriting, image production, versioning of ads, and creative testing at scales not achievable by hand. Personalization alters messages on an individual basis rather than group basis and converts one campaign idea to multiple versions automatically. Optimization processes A/B tests on results and deploys winners instantaneously, without any human involvement.
The technology is not quite complete. American Eagle CMO Craig Brommers also pointed to “generic creative” generated by AI that can harm brand distinctiveness. Human intervention is still greatly required to ensure quality and guide strategy.
How Leading Brands Implemented Generative AI
The most successful implementations combine AI capabilities with strong brand strategy and human creativity.
Coca-Cola: Multi-Channel AI Integration
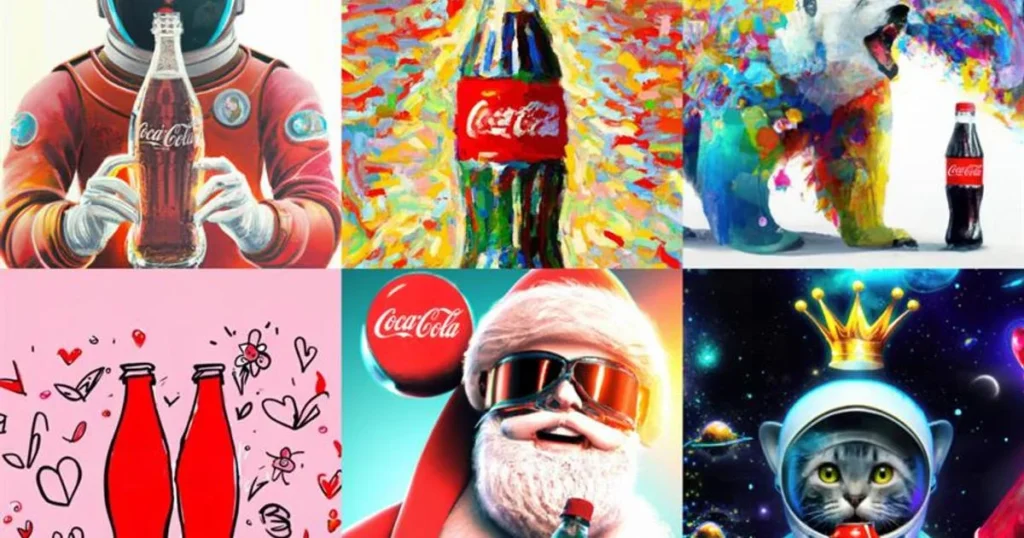

Coca-Cola partnered on the “Create Real Magic” initiative with Bain & Company and OpenAI. The initiative encouraged the participants to combine the classical Coca-Cola advertising art with ChatGPT and DALL-E to come up with new works. Coca-Cola used FIFA World Cup to deploy AI platforms to produce customized content on football supporters by creating more than 120,000 personalized videos with consumers’ names and photographs embedded within Coca-Cola brand templates.
For the Christmas season of 2024, Coca-Cola created “Create Real Magic” platform consisting of the 3D digital twin of its original 1931 Santa powered by conversational AI to converse with individuals in 26 languages. The campaigns demonstrated how AI enables experiences previously impossible with traditional production methods.
Nike: AI-Powered Product Development and Storytelling

Nike’s chief innovation officer revealed they have been training a proprietary AI model on private athlete performance data, using tools like 3D printing, VR, and computational design to create prototypes at record speed. Nike developed a “Never Done Evolving” ad involving an AI-created game of tennis between young Serena Williams from her maiden Grand Slam back in 1999 and contemporary Serena Williams from the Australian Open held in 2017 to mark Nike’s 50th anniversary.
The Nike Fit app is an amalgamation of AI and AR and allows users to scan feet to receive perfect shoe recommendations with precise measurements. These deployments demonstrate how artificial intelligence supports innovative opportunities more than replacing human judgment.
Cadbury: Hyper-Personalized Celebrity Marketing

Cadbury India also built a campaign, which enabled shop owners to create their own video advertisements that included Bollywood actor Shah Rukh Khan, where AI would adjust the voice and likeness of the actor to use the name of specific stores. The campaign provided small businesses with a reach the size of celebrities without the budgets of celebrities, which proves that AI can be used to personalize on an unprecedented scale.
H&M: Digital Twins for Fashion Marketing

In their advertisement campaigns, H&M developed AI-generated 30 real-life human models in the form of digital twins, with Chief Creative Officer Jorgen Andersson saying that this is meant to improve their creative process but the remaining aspect of their approach is to be human-centric.
Heinz: AI-Driven Visual Branding

Heinz ran a campaign through DALL-E and other generative AI programs, requesting AI to draw ketchup, and the resulting images had a graphic similarity to the iconic package bottle that is used in social media, digital advertisements, and packaging. The campaign strengthened the brand identity by the automatic recognition of their visual dominance in this category by AI.
Nutella: Mass Personalization at Shelf Level

Finding a new way to make product packaging a collectible experience, Nutella commissioned its generative algorithms to design seven million unique labels on jars, which sold out.
Etsy: AI-Powered Gift Discovery
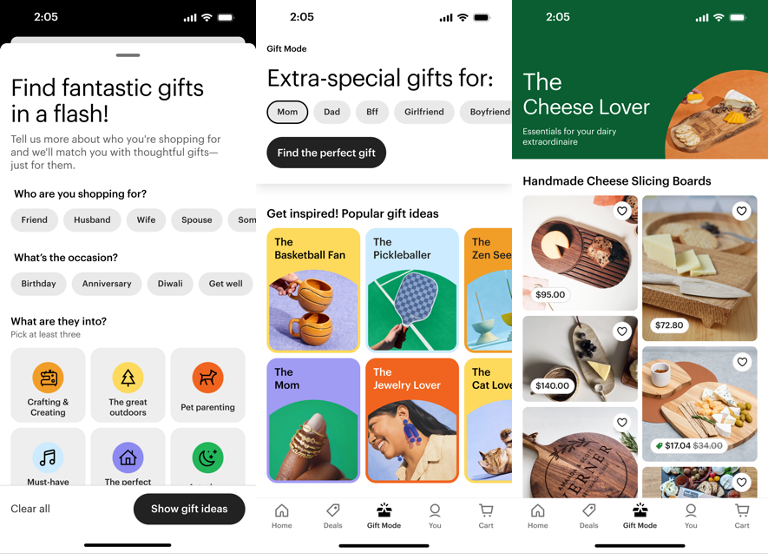
Etsy launched the “gift mode” which gives the recipient a persona one of the over 200 personas depending on the preferences of the user and provides customized gift recommendations. The technology also addressed one of the common challenges facing e-commerce, which is making it easy to make decisions as a customer.
Real-World Marketing Applications
The applications spread across every content format and marketing function.
1. Content Creation at Scale
Generative AI is not confined to text and allows marketers to make videos, music, three-dimensional content, and other interactive content with minimal effort. Gartner reports that brands are turning to AI to augment, accelerate, and develop new content at a rapid rate, written blogs and short-form videos, and visuals of products. In 2018, even platforms such as the AI writer at Alibaba were already able to create an engaging copy with minimal human input. The technology has since grown much since that time.
2. Personalization Beyond Demographics
Personalization is evolving from general experiences based on demographics to highly individual interactions based on unique search intent, preferences, and context. McKinsey warns brands will need to balance hyper-personalized marketing, potentially boosting ROAS by up to 25%, with strong privacy and ethical guardrails.
3. Campaign Optimization and Testing
Both Meta and Google Ads have made dynamic headlines and creative, AI-generated suggestions, and dynamic remarketing available, having massive impacts on performance and success of digital marketing campaigns. Campaigns are evolving beyond basic demographic targeting, with AI now enabling emotion-based, contextual targeting driven by real-time sentiment analysis.
4. First-Party Data and AI Integration
AI analyzes patterns like shopping habits, preferred communication channels, and engagement trends without using cookies, combining first-party data with demographic or geographic information and adjusting audiences on the fly based on new data or changes in customer behavior.
Measurable Business Outcomes
Survey data and industry reports reveal which benefits are real versus imagined.
1. ROI and Revenue Impact
Brands using AI-driven personalization capture 5-15% incremental revenue and gain 10-30% efficiency in marketing spend. Retailers experimenting with AI-powered targeted campaigns achieve 10% to 25% higher returns on ad spending.
2. Adoption and Satisfaction
Bain’s survey of more than 180 large US companies found that 27% of respondents said generative AI had exceeded or far exceeded expectations for marketing. Over 37% of marketing teams have embraced AI as a core part of their strategy.
3. Consumer Behavior Changes
Statista estimates that more than 90 million people are expected to use AI as their primary form of search by 2027. Microsoft research found that purchasing behaviors increased by 53% within 30 minutes of a Copilot interaction.
4. Content Performance
Over 80% of the content watched on Netflix is driven by its AI-powered recommendation system, and this informs their social media advertising.
Strategic Value Areas for Implementation
Four marketing areas offer the greatest potential for generative AI deployment:
- Workflow simplification streamlines creative concept drafting, image production, content translation, brand compliance checks, and asset tagging.
- Content creation and personalization automates copywriting, image production, ad versioning, and other creative tasks at scales impossible with human teams alone.
- Customer insights and intelligence provides real-time analytics and segmentation, with AI simulating customer behavior and predicting future needs.
- Campaign optimization and testing enables continuous optimization rather than periodic testing cycles, with AI analyzing results and implementing winners automatically.
Key Implementation Challenges
Real barriers exist that marketing teams must address for successful adoption.
Quality and Authenticity Concerns
Consumers consistently rated AI-generated video advertising more “annoying,” “boring,” and “confusing” than conventional ads, according to a study published by NielsenIQ (NIQ) in December 2024. American Eagle CMO Craig Brommers spoke of concerns that AI results in “generic creative” that could affect authenticity of brands prioritizing diversity and inclusion. Relying too heavily on AI-generated content can foster a sense of inauthenticity amongst your audience and may alienate them.
Platform and Tool Overwhelm
“Overwhelming” was a descriptor repeated by several experts, who expect that 2026 will see some culling as companies creating industry-specific and well-rounded generative AI products rise to the top. Platforms that are transparent around how AI models are trained could curry favor with risk-averse marketers.
Intellectual Property and Legal Concerns
For larger marketers protective of their intellectual property, forking over valuable material to large language models and machine-learning algorithms is still a daunting prospect. “Ownership is the biggest piece of this, and it’s still unclear,” with concerns about billion dollar brands losing specifics about their brand and plans.
Diversity and Bias Issues
“There’s a real diversity and inclusion aspect to this story. AI is pulling from everything that exists and isn’t always able to do the best job of representation,” according to Megan Belden, vice president for NIQ’s Bases Advertising.
Best Practices from Leading Implementations
Companies achieving measurable success follow specific patterns.
1. Balance Automation with Human Oversight
Considerable human oversight should exist on what AI produces and what the finished product looks like, with talented marketers fine-tuning AI generated content to ensure it is of great quality and fits the business aesthetic, tone, and desired perception.
Marketers should adopt a hybrid approach using AI tools to scale processes while maintaining the authenticity, emotional connection and depth audiences relate to.
2. Start with Low-Risk Applications
Generative AI may still be underbaked when it comes to realizing a final creative product, but its influence over other aspects of the production pipeline will climb in 2026, with early-stage tasks like briefing, research and storyboarding seeing a boost.
3. Focus on Brand-Specific Training
Coca-Cola worked with three different studios with creative technologists who are engineers, early adopters and storytellers, giving them their 1990s film as a brief because they knew they had rights to use that as the prompt.
4. Set Measurable Goals
CMOs should set measurable, ambitious targets (whether operational, customer-centered, or financial) and hold their teams accountable rather than focusing on individual use cases.
Comparison: Traditional vs AI-Enhanced Marketing
| Dimension | Traditional Marketing | AI-Enhanced Marketing |
| Campaign Development | 4-8 weeks | 2-5 days |
| Content Variations | 3-5 manually created | 100+ auto-generated |
| Personalization | Segment-level (10-20 groups) | Individual-level (thousands) |
| Testing Cycles | 2-4 weeks per test | Real-time continuous |
| ROAS Improvement | Baseline | 10-25% higher |
| Revenue Lift | Standard | 5-15% incremental |
| Marketing Efficiency | Baseline | 10-30% improvement |
Emerging Trends for 2026 and Beyond
Three major shifts are reshaping how marketers use generative AI.
Multimodal AI Integration
Multimodal AI integrates contextual information from different modalities to provide richer insights, with systems generating content across modalities like text-to-image generation, video summaries from text descriptions, and audio generation from written scripts. RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) allows businesses to customize AI responses using their own data, supplementing generic training with company and market specific insight.
Voice and Conversational AI
As AI-powered voice assistants, smart displays, and wearables become more integrated into everyday life, marketing will need to evolve beyond static content, with voice search optimization, AI-generated interactive experiences, and AI-driven customer interactions redefining how brands communicate.
Predictive Analytics and Customer Intelligence
AI-driven insights allow marketers to track engagement, sentiment, and consumer preferences with precision and speed, with AI’s ability to provide deep, actionable insights into consumer behavior growing exponentially. New company Aaru’s flagship model “Lumen” configures audiences to predict customer persona behavior using a multi-agent approach to create simulations based on events that haven’t yet happened.
Practical Implementation Framework
Follow these steps based on successful brand deployments:
- Analyze the existing capabilities through auditing the current AI use, detecting gaps, and analyzing team preparedness to accept AI.
- The first step should be high-impact, low-risk, such as content drafting, image variations, or research work, before the use of AI in customer-facing campaigns is deployed.
- Invest in training teams in responding quickly to engineering, quality management, ethical use of AI, and thinking more strategically of instances where AI would be useful and instances where human creativity is necessary.
- Standardize data infrastructure, clean up data sources and develop systems on AI to access quality information.
- Establish brand principles with respect to AI, such as voice parameters, visual style principles, and messaging principles to which AI should adhere.
- Measure impact in a strict manner by monitoring the productivity improvements, content performance, campaign ROI and team satisfaction on channel, creative, and segment level.
- Always have human control over how the AI-generated content is reviewed before being published in order to identify mistakes and maintain brand continuity.
The Path Forward
Generative AI is already shifting the need in marketing and more sophisticated groups are already considering the future of the partner ecosystem, bracing the end of link-based search, and ideating what marketing to bots could look like.
The future of AI systems is not only to perform a task but also to influence the marketing strategy and the creative decision-making process in 2026. The adoption of AI in marketing is at a crunching point, and what used to be seen as being in the leading edge is now a must to remain relevant.
The brands that will win in 2026 are not always the ones that employ the most fancy AI tools. It is they who were able to calculate how to integrate AI efficiency and human creativity and strategic thinking and preserve the brand authenticity and customer trust.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does AI marketing actually improve campaign performance?
The returns of advertisements on retailers trying AI-based targeted campaigns are 10 to 25% higher, and the returns of personalization with AI-based processes of brands are 5-15 % and 10-30 % on returns of marketing expenditures. The increase in performance depends on the quality of implementation and the selection of the use case.
What are the biggest risks of using AI in marketing?
Consumers consistently rated AI-generated video advertising more “annoying,” “boring,” and “confusing” than conventional ads according to NielsenIQ research. Concerns also include generic creative that affects brand authenticity, diversity and inclusion issues where AI pulls from everything that exists without proper representation, and intellectual property concerns about sharing brand specifics with AI models.
How are consumers responding to AI-generated advertising?
Consumer enthusiasm for generative AI deflated in 2024 as ads made with the technology were repeatedly subject to derision, with tech giants like Google and Apple pulling commercials that sounded dystopian alarms while Coca-Cola’s holiday campaign received particularly contentious reception. However, success varies based on execution quality and brand authenticity.
What percentage of marketing teams currently use AI?
According to the IAB 2026 Video Ad Spend & Strategy Report, 86% of advertisers say they are using or will use generative AI to generate video ads, and more than 37 percent of marketing teams have now adopted AI as part of their core strategy. The rate of adoption is still growing.
Will AI replace human marketers and creative professionals?
Much of the heavy lifting can be done by AI, but talented marketers with a keen sense of judgment can tweak AI-generated content to make it of great quality and with the right fit of the business aesthetics, tone, and perceptions. AI will probably become a co-creator and bear heavy lifting as human teams concentrate on strategy and emotional richness of campaigns. The technology does not replace human creativity and strategic thinking but augments it.